tethne.analyze package¶
Submodules¶
tethne.analyze.collection module¶
Methods for analyzing GraphCollections.
algorithm |
Apply a method from NetworkX to all networkx.Graph objects in the GraphCollection G. |
attachment_probability |
Calculates the attachment probability for each node at each time-step. |
connected |
Performs analysis methods from networkx.connected on each graph in the collection. |
delta |
|
node_global_closeness_centrality |
-
tethne.analyze.collection.algorithm(G, method_name, **kwargs)[source]¶ Apply a
methodfrom NetworkX to all networkx.Graph objects in theGraphCollectionG.For options, see the list of algorithms in the NetworkX documentation. Not all of these have been tested.
Parameters: G :
GraphCollectionThe
GraphCollectionto analyze. The specified method will be applied to each graph inG.method_name : string
Name of a method in NetworkX to execute on graph collection.
**kwargs
A list of keyword arguments that should correspond to the parameters of the specified method.
Returns: results : dict
Indexed by element (node or edge) and graph index (e.g.
date).Raises: ValueError
If no such method exists.
Examples
Betweenness centrality: (
Gis aGraphCollection)>>> from tethne.analyze import collection >>> BC = collection.algorithm(G, 'betweenness_centrality') >>> print BC[0] {1999: 0.010101651117889644, 2000: 0.0008689093723107329, 2001: 0.010504898852426189, 2002: 0.009338654511194512, 2003: 0.007519105636349891}
-
tethne.analyze.collection.attachment_probability(G, raw=False)[source]¶ Calculates the attachment probability for each node at each time-step.
The attachment probability for a node at a particular graph state
tis the probability that the next edge added to the graph will accrue to that node. The MLE for attachment probability is thus the observed fraction of all new edges in graph statet + 1that accrue to a particular node.Note that values will only be calculated for nodes present in state
t. In other words, if int + 1a new node is introduced who also accrues new edges, that node will not appear in the results for statet.Parameters: G :
GraphCollectionraw : bool
(default:
False) IfTrue, nodes are represented by their integer ids inG, rather than their label.Returns: probs : dict
Keyed by index in
G, and then by node. Ifrawis True, node keys will be integer indices from the GraphCollection’snode_index.Examples
>>> from tethne.readers.wos import read >>> corpus = read("/path/to/my/data") >>> from tethne import coauthors, GraphCollection >>> collection = GraphCollection(corpus, coauthors) >>> from tethne.analyze.collection import attachment_probability >>> probs = attachment_probability(collection)
-
tethne.analyze.collection.connected(G, method_name, **kwargs)[source]¶ Performs analysis methods from networkx.connected on each graph in the collection.
Parameters: G :
GraphCollectionThe
GraphCollectionto analyze. The specified method will be applied to each graph inG.method : string
Name of method in networkx.connected.
**kwargs : kwargs
Keyword arguments, passed directly to method.
Returns: results : dict
Keys are graph indices, values are output of method for that graph.
Raises: ValueError
If name is not in networkx.connected, or if no such method exists.
tethne.analyze.corpus module¶
Methods for analyzing Corpus objects.
burstness |
Estimate burstness profile for the topn features (or flist) in feature. |
feature_burstness |
Estimate burstness profile for a feature over the 'date' axis. |
sigma |
Calculate sigma (from Chen 2009) for all of the nodes in a GraphCollection. |
-
tethne.analyze.corpus.burstness(corpus, featureset_name, features=[], k=5, topn=20, perslice=False, normalize=True, **kwargs)[source]¶ Estimate burstness profile for the
topnfeatures (orflist) infeature.Uses the popular burstness automaton model inroduced by Kleinberg (2002).
Parameters: corpus :
Corpusfeature : str
Name of featureset in
corpus. E.g.'citations'.k : int
(default: 5) Number of burst states.
topn : int or float {0.-1.}
(default: 20) Number (int) or percentage (float) of top-occurring features to return. If
flistis provided, this parameter is ignored.perslice : bool
(default: False) If True, loads
topnfeatures per slice. Otherwise, loadstopnfeatures overall. Ifflistis provided, this parameter is ignored.flist : list
List of features. If provided,
topnandpersliceare ignored.normalize : bool
(default: True) If True, burstness is expressed relative to the hightest possible state (
k-1). Otherwise, states themselves are returned.kwargs : kwargs
Parameters for burstness automaton HMM.
Returns: B : dict
Keys are features, values are tuples of ( dates, burstness )
Examples
>>> from tethne.analyze.corpus import burstness >>> B = burstness(corpus, 'abstractTerms', flist=['process', 'method'] >>> B['process'] ([1990, 1991, 1992, 1993], [0., 0.4, 0.6, 0.])
-
tethne.analyze.corpus.feature_burstness(corpus, featureset_name, feature, k=5, normalize=True, s=1.1, gamma=1.0, **slice_kwargs)[source]¶ Estimate burstness profile for a feature over the
'date'axis.Parameters: corpus :
Corpusfeature : str
Name of featureset in
corpus. E.g.'citations'.findex : int
Index of
featureincorpus.k : int
(default: 5) Number of burst states.
normalize : bool
(default: True) If True, burstness is expressed relative to the hightest possible state (
k-1). Otherwise, states themselves are returned.kwargs : kwargs
Parameters for burstness automaton HMM.
-
tethne.analyze.corpus.sigma(G, corpus, featureset_name, B=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Calculate sigma (from Chen 2009) for all of the nodes in a
GraphCollection.You can set parameters for burstness estimation using
kwargs:Parameter Description s Scaling parameter ( > 1.)that controls graininess of burst detection. Lower values make the model more sensitive. Defaults to 1.1. gamma Parameter that controls the ‘cost’ of higher burst states. Defaults to 1.0. k Number of burst states. Defaults to 5. Parameters: G :
GraphCollectioncorpus :
Corpusfeature : str
Name of a featureset in corpus.
Examples
Assuming that you have a
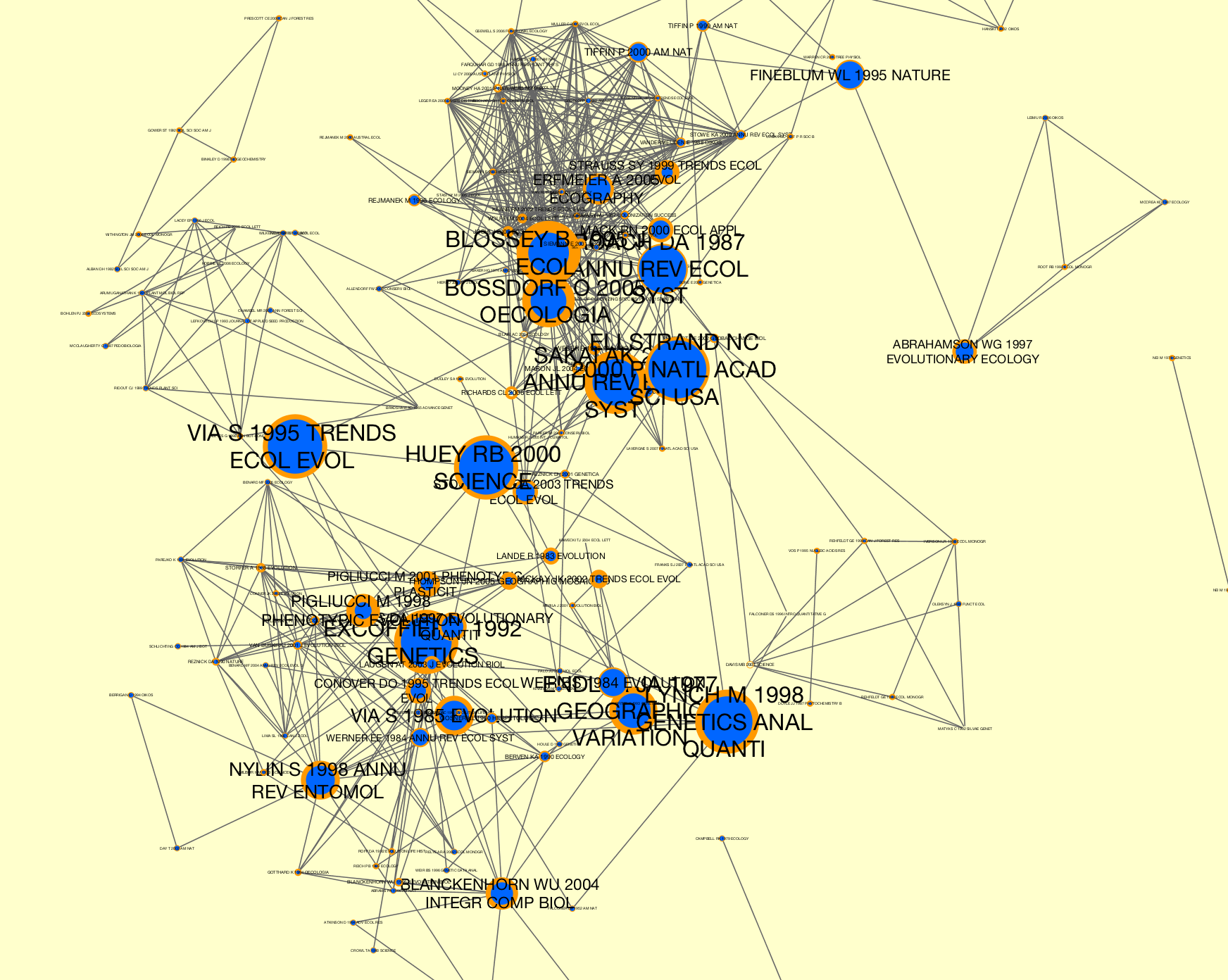
Corpusgenerated from WoS data that has been sliced bydate.>>> # Generate a co-citation graph collection. >>> from tethne import GraphCollection >>> kwargs = { 'threshold':2, 'topn':100 } >>> G = GraphCollection() >>> G.build(corpus, 'date', 'papers', 'cocitation', method_kwargs=kwargs) >>> # Calculate sigma. This may take several minutes, depending on the >>> # size of your co-citaiton graph collection. >>> from tethne.analyze.corpus import sigma >>> G = sigma(G, corpus, 'citations') >>> # Visualize... >>> from tethne.writers import collection >>> collection.to_dxgmml(G, '~/cocitation.xgmml')
In the visualization below, node and label sizes are mapped to
sigma, and border width is mapped tocitations.
tethne.analyze.features module¶
Methods for analyzing featuresets.
cosine_distance |
|
cosine_similarity |
Calculate cosine similarity for sparse feature vectors. |
distance |
|
kl_divergence |
Calculate Kullback-Leibler distance. |
-
tethne.analyze.features.angular_similarity(F_a, F_b)[source]¶ Calculate the angular similarity for sparse feature vectors.
Unlike cosine_similarity, this is a true distance metric.
Parameters: F_a :
FeatureF_b :
FeatureReturns: similarity : float
Cosine similarity.
-
tethne.analyze.features.cosine_similarity(F_a, F_b)[source]¶ Calculate cosine similarity for sparse feature vectors.
Parameters: F_a :
FeatureF_b :
FeatureReturns: similarity : float
Cosine similarity.
tethne.analyze.graph module¶
Methods for network analysis.
global_closeness_centrality |
Calculates global closeness centrality for one or all nodes in the network. |
-
tethne.analyze.graph.global_closeness_centrality(g, node=None, normalize=True)[source]¶ Calculates global closeness centrality for one or all nodes in the network.
See
node_global_closeness_centrality()for more information.Parameters: g : networkx.Graph
normalize : boolean
If True, normalizes centrality based on the average shortest path length. Default is True.
Returns: C : dict
Dictionary of results, with node identifiers as keys and gcc as values.
Module contents¶
Methods for analyzing Corpus, GraphCollection, and
networkx.Graph objects.
collection |
Methods for analyzing GraphCollections. |
corpus |
Methods for analyzing Corpus objects. |
features |
Methods for analyzing featuresets. |
graph |
Methods for network analysis. |